Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMJ-TMD) represent a complex and often misunderstood category of conditions affecting millions worldwide. These disorders, involving the jaw joint and the muscles responsible for jaw movement, can lead to a spectrum of symptoms that significantly impact daily life, from eating and speaking to overall comfort and well-being. Understanding TMJ-TMD is not just about recognizing its physical manifestations; it’s about comprehending its broader effects on oral health, quality of life, and mental well-being.
This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the complexities of TMJ-TMD, providing an in-depth look into what this condition entails, its varied symptoms, potential causes, and effective treatment strategies. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, suspect you might have TMJ-TMD, or are seeking more information to manage your condition better, this article offers valuable insights into navigating life with TMJ-TMD, embracing both medical and self-care approaches to treatment and management.
What Is TMJ-TMD?
Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMJ-TMD) are a group of conditions that affect the temporomandibular joint, the muscles that move the jaw, and the surrounding nerves. This joint, one of the most complex in the human body, acts like a sliding hinge connecting the jawbone to the skull. TMJ-TMD can cause a range of issues, from mild discomfort to severe pain and dysfunction, impacting the ability to chew, speak, and even yawn comfortably. The disorders can affect one or both sides of the face and often involve a combination of joint and muscle problems, making diagnosis and treatment a multifaceted challenge.
Signs and Symptoms of TMJ-TMD
The symptoms of TMJ-TMD can vary greatly in severity and manifestation, including:
- Jaw Pain and Tenderness: Often the most noticeable symptom, this can be felt in the jaw joint area, ears, neck, and sometimes the shoulders.
- Difficulty in Jaw Movement: This may include pain or difficulty in opening the mouth wide, jaw locking in an open or closed position, and a feeling of the jaw getting “stuck.”
- Noises from the Joint: Clicking, popping, or grating sounds in the jaw joint when opening or closing the mouth or chewing.
- Headaches and Earaches: Pain that radiates to other areas of the face and head.
- Facial Pain and Fatigue: Due to strain on the muscles involved in jaw movement.
These symptoms can lead to secondary issues such as difficulty eating, chronic headaches, and in some cases, significant lifestyle disruptions.
Causes and Diagnosis of TMJ-TMD
TMJ-TMD can arise from various factors, often making the exact cause challenging to pinpoint. Possible causes include:
- Physical Factors: Such as injury to the jaw, joint arthritis, or wear and tear due to aging.
- Dental Factors: Misaligned bite, teeth grinding (bruxism), or prolonged dental work.
- Psychological Factors: Stress and anxiety can lead to teeth grinding and jaw clenching, exacerbating TMJ-TMD symptoms.
- Habitual Factors: Such as habitual gum chewing, nail-biting, or chin resting.
Diagnosing TMJ-TMD typically involves a comprehensive examination by a dentist or a maxillofacial specialist. This may include reviewing the patient’s medical history, conducting a physical examination of the jaw and face, and using imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to assess the condition of the jaw and surrounding structures.
Treatment Options for TMJ-TMD
Treating TMJ-TMD effectively often requires a combination of therapies tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and underlying causes. The most common treatment options include:
- Medications: For immediate relief, medications such as pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and muscle relaxants can be effective. In some cases, tricyclic antidepressants are prescribed for pain relief, sleep disturbances, and bruxism control.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen jaw muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. This may include exercises to stretch and strengthen the jaw, massage, and the use of heat or cold to alleviate discomfort.
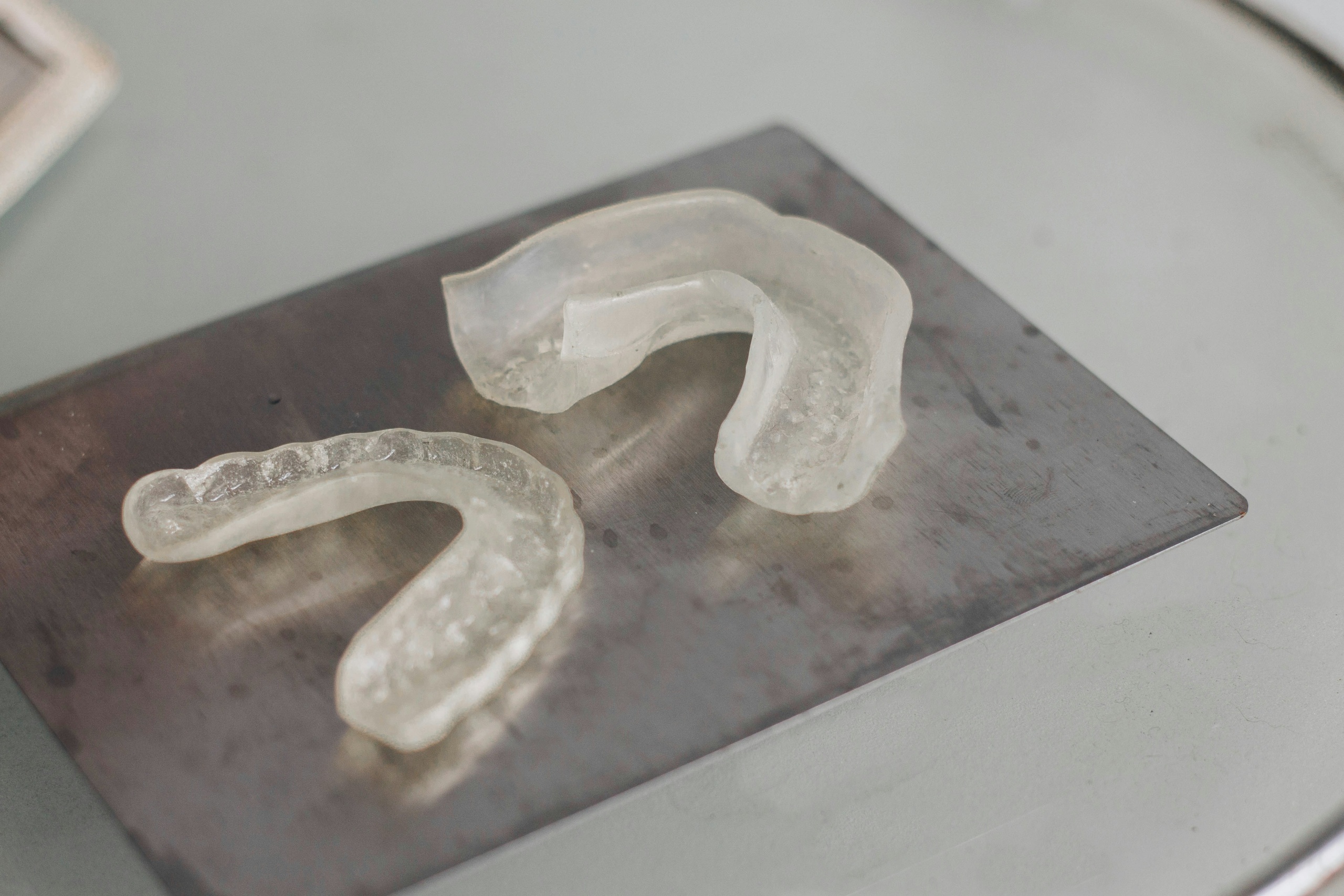
- Occlusal Appliances: Mouthguards or splints can be used, particularly at night, to reduce teeth grinding and jaw clenching, thus alleviating pressure on the TMJ.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases where conservative treatments don’t provide relief, surgical options such as arthrocentesis, TMJ arthroscopy, or open-joint surgery might be considered.
- Alternative Therapies: Some patients find relief through acupuncture, biofeedback, or relaxation techniques to manage stress-related TMJ symptoms.
Self-Care and Pain Relief for TMJ-TMD
Self-care practices are vital in managing TMJ-TMD symptoms:
- Jaw Exercises: Regularly practicing jaw exercises can increase mobility, reduce stiffness, and alleviate pain.
- Stress Reduction: Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress, a common trigger for TMJ-TMD symptoms.
- Dietary Adjustments: Eating soft foods and cutting food into smaller pieces can reduce strain on the jaw.
- Avoiding Harmful Habits: Habits like gum chewing, nail-biting, or leaning on the jaw can aggravate TMJ-TMD and should be avoided.
Preventing TMJ-TMD and Reducing Recurrence
Preventing TMJ-TMD or reducing the risk of its recurrence involves lifestyle adjustments and awareness of jaw health:
- Mindful Jaw Usage: Be conscious of jaw movements and avoid overextending the jaw, such as with wide yawning or loud singing.
- Proper Dental Care: Regular dental check-ups can help identify and address potential issues like misaligned teeth that might contribute to TMJ-TMD.
- Ergonomics at Work: Ensure that your workstation is ergonomically set up to reduce strain on the body, including the jaw.
- Regular Exercise and Good Posture: Maintain overall physical health and a good posture to reduce tension in the muscles around the jaw.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to TMJ-TMD Management
Successfully managing TMJ-TMD requires a holistic approach that combines professional medical treatments with practical self-care strategies. Understanding this condition’s multifaceted nature is key to addressing the diverse range of symptoms it presents. Whether through medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, or in some cases, surgical interventions, each treatment plan should be tailored to meet the individual’s specific needs.
Equally important is the role of self-care in alleviating TMJ-TMD symptoms. Regular jaw exercises, stress reduction techniques, dietary adjustments, and avoiding harmful jaw habits can significantly improve quality of life for those affected by this disorder. Furthermore, preventive measures like maintaining good oral health, ergonomic practices, and mindfulness of jaw movements play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of recurrence or exacerbation of symptoms.
In navigating the journey of TMJ-TMD management, remember that patience and persistence are vital. With the right combination of treatments and self-care, individuals with TMJ-TMD can achieve significant relief and enjoy a better quality of life. Always consult with healthcare professionals to create a personalized and effective management plan, and embrace each step towards recovery with confidence and optimism.