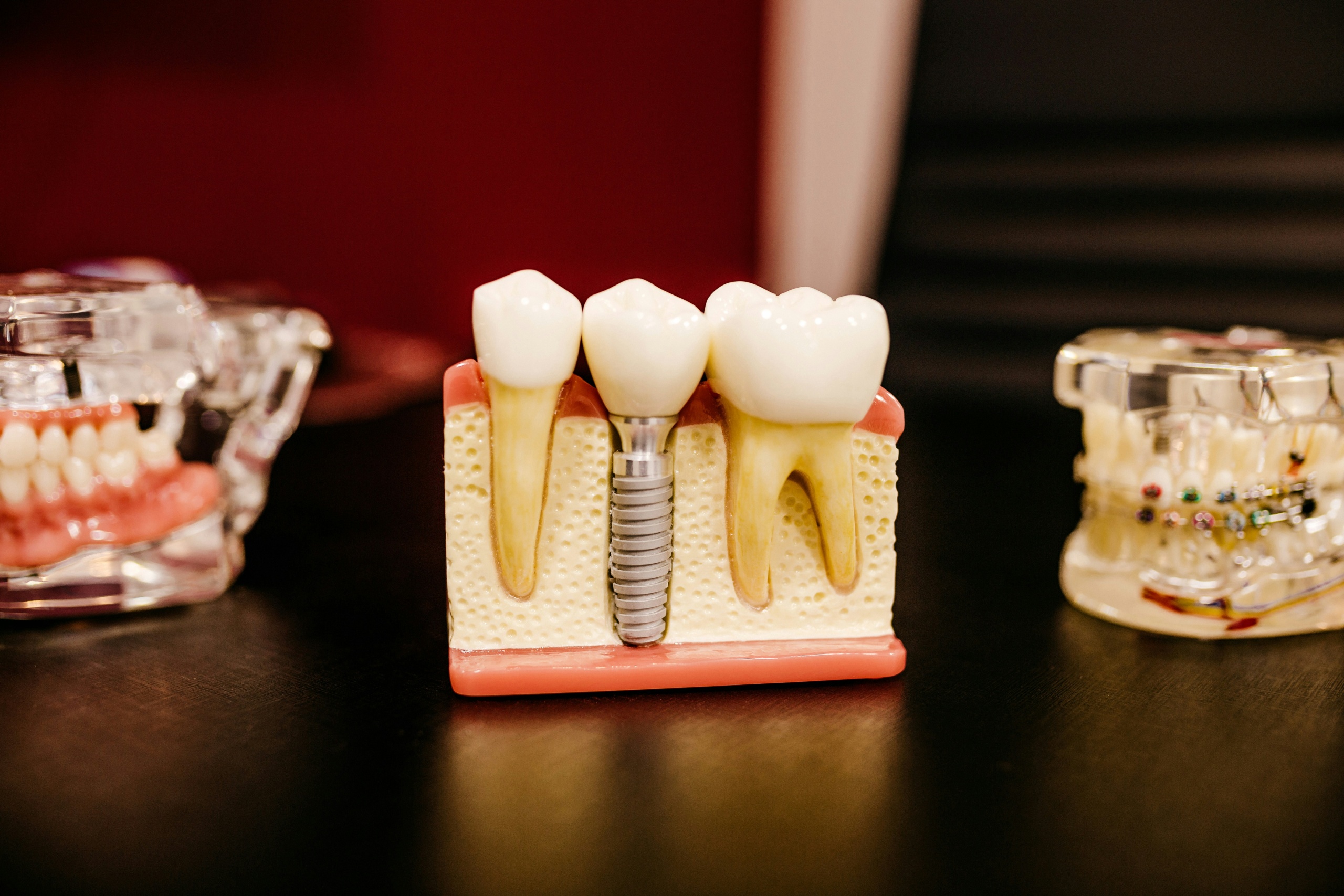
A dental bridge usually lasts between 5 and 15 years. With excellent oral hygiene, regular checkups, and careful habits, some bridges can last 20 years or more. The exact lifespan depends on the bridge type, materials used, and the health of supporting teeth and gums. A dental bridge is both a health investment and a cosmetic solution.
If you’re wondering about dental crowns and bridges in Millburn, NJ, longevity is probably on your mind. A bridge is a huge investment; both in your oral health and your looks. Let’s take a look at what the research shows about durability, complications, and care. Armed with this knowledge, you can set realistic expectations and extend the life of your restoration.
What Is the Average Lifespan of a Dental Bridge?
The widely accepted estimate for a dental bridge is 5–15 years. But, survival studies provide more precise numbers. Short-span bridges of three or four units tend to perform better over time, with about 91 percent lasting at least 5 years, 68 percent surviving 10 years, and 34 percent still in place at 15 years.
By contrast, long-span bridges of five units or more show slightly lower success rates. These restorations average 85 percent survival at 5 years, 50 percent at 10 years, and only 18 percent at 15 years. These numbers show how much the bridge design matters in how it distributes stress across the surrounding teeth.
What Factors Affect the Lifespan of a Dental Bridge?
The type of bridge used plays a major role. Traditional designs supported by crowns on both sides remain the most common. Cantilever bridges, which anchor to one tooth, are more prone to complications because of the uneven load. Maryland bridges are less invasive but can debond more easily. Implant-supported bridges often provide the greatest long-term stability since they don’t rely on natural teeth for support.
Implant-supported bridges often provide the greatest long-term stability since they don’t rely on natural teeth for support. Learn more about how implant bridges work here.
Location in the mouth also matters. Upper-arch long-span bridges tend to fail at a higher rate than those placed in the lower arch. The biting forces and bone supports are different.
Patient behavior and oral health round out the picture. Gum disease, decay of supporting teeth, and habits like grinding or chewing on ice all shorten the life of a bridge. But, consistent home care and regular dental checkups can add years to a restoration’s lifespan.
How Do Materials Affect Bridge Longevity?
One of the most important choices in planning a bridge is the material. Each option comes with its own strengths, esthetics, and long-term performance.
| Material | Strength & Durability | Esthetics | Common Uses | Survival Trends | Notes |
| Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) | Very strong, proven track record | Good, but gray metal may show | Most spans, especially back teeth | High survival; long-term gold standard | Reliable, less natural than ceramics |
| Lithium Disilicate | Strong, best for short spans | Excellent, highly natural | Single crowns, short bridges | Over 90% survival at 5 years | Great for front teeth, not ideal for long spans |
| Zirconia | Durable and fracture-resistant | Excellent, natural look | Both anterior and posterior bridges | Good survival, but higher chipping risk | Balance of esthetics + strength |
How Long Do PFM Bridges Last?
Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) bridges remain one of the most time-tested solutions in dentistry. Their strength lies in the combination of a durable metal framework with porcelain that mimics natural enamel. The mixture makes them more reliable in areas that withstand high chewing forces, such as the molars.
PFMs can last 10–15 years or more, with many still functioning well beyond 20 years when patients maintain excellent oral hygiene. These bridges have been studied more extensively than newer materials. They’re the benchmark for long-term data.
One drawback is cosmetic. Over time, the gum tissue may recede slightly, exposing a thin metal line at the edge of the crown. Some patients also notice that PFMs do not reflect light as naturally as all-ceramic restorations. Still, for patients prioritizing durability, especially for longer spans, PFM bridges remain a top choice.
How Long Do Lithium Disilicate Bridges Last?
Lithium disilicate bridges have become a favorite in cosmetic dentistry thanks to their translucency and natural appearance. The glass-ceramic material closely mimics the look of enamel. As a result, many patients choose it for their front teeth, where esthetics are most important.
Studies report survival rates exceeding 90 percent at 5 years for crowns and short-span bridges. Patients often find that these restorations blend seamlessly into their smile, making them almost indistinguishable from natural teeth.
The main limitation is strength over longer spans. While lithium disilicate is strong for single units, it can fracture more easily than zirconia or PFMs when used in multi-unit bridges under heavy biting forces. That said, for cosmetic cases in the front of the mouth, it strikes an excellent balance between beauty and functionality.
Patients in Millburn who focus on appearance often choose lithium disilicate for visible areas of their smile. As long as they’re taken care of, these bridges will provide many years of service.
How Long Do Zirconia Bridges Last?
Zirconia bridges are known for their combination of durability and esthetics. Unlike PFMs, they don’t rely on a metal base. Despite this, they offer fracture resistance that rivals or surpasses traditional options. This makes zirconia a versatile choice for both front and back teeth.
These bridges perform reliably in both short and long spans. Many patients appreciate that zirconia can be shaded to match natural teeth more closely than older ceramic systems. But, there is a somewhat higher rate of chipping in the veneering porcelain compared to PFMs.
For patients who want a modern solution that looks natural and holds up under daily chewing, zirconia bridges offer a strong option. They are particularly popular for patients seeking a balance between esthetics and strength. The potential gumline discoloration sometimes associated with metal-based restorations won’t be an issue.
What Are the Most Common Complications With Dental Bridges?
Over time, certain issues tend to appear more frequently than others. Studies highlight these as the most common problems:
- Chipping or fracture of porcelain, especially in long-span bridges after 10 or more years.
- Loss of retention, where the cement loosens and the bridge shifts or comes off.
- Decay of abutment teeth, caused by bacteria trapped around or under crowns.
- Framework fractures, often in larger bridges under high stress.
While some issues can be repaired, others need full replacement. Early detection during dental visits is the best way to prevent minor problems from snowballing into more expensive, invasive issues.
How Can You Make Your Dental Bridge Last Longer?
Patients have a direct influence on how long their dental bridge will last. Keeping your gums healthy is especially important for bridge longevity. Here are some practical tips for keeping gums healthy:
- Brush twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss under the bridge daily with floss threaders or a water flosser.
- Avoid hard foods like ice, hard candy, or nuts that can stress the porcelain.
- Use a nightguard if you grind your teeth. You can also explore other strategies for preventing teeth grinding.
- Schedule regular checkups to catch problems before they need replacement.
Following these steps consistently can add years to the lifespan of your dental bridge.
When Should You Replace a Dental Bridge?
Nothing lasts forever, not even your dental bridge. Even the most durable dental bridge will eventually reach the end of its service life. Replacement does not always mean failure. It can simply reflect normal wear after many years. Common reasons for replacement include looseness or rocking of the bridge, visible cracks or fractures, discomfort around supporting teeth, or changes in how your bite feels.
Decay under the crowns is another frequent reason. If bacteria infiltrate the abutment teeth, they can compromise the foundation of the bridge. Gum recession may also expose vulnerable areas over time. If you’re unsure what this means, you can read more about gum recession. In some cases, a bridge can be recemented or repaired, but if the supporting teeth are too damaged, a full replacement may be necessary.
Many patients ask whether a bridge can last a lifetime. In rare cases, with meticulous care and favorable conditions, it can. More commonly, yet, replacement after 10–15 years is expected. Planning for this eventuality allows you to protect your oral health and budget accordingly.
Dental Crowns and Bridges in Millburn NJ — Choosing the Right Option
For patients in Millburn, choosing the right bridge involves balancing strength, esthetics, and long-term needs. PFMs continue to offer unmatched durability, lithium disilicate excels in cosmetic areas, and zirconia bridges provide a modern blend of both. The decision often comes down to where the bridge will be placed, how long it needs to last, and the patient’s priorities.
Working with a dentist who understands all three materials ensures a personalized approach. Each option has its advantages, and an experienced dentist can guide you toward the one best suited to your smile and lifestyle.
Key Takeaways for Dental Crowns and Bridges in Millburn, NJ
Dental bridges typically last 5–15 years, but their lifespan can extend much longer with the right care and materials. Shorter spans, good oral hygiene, and careful monitoring help many bridges remain functional well beyond the average.
PFM bridges remain the most proven, lithium disilicate offers unmatched beauty, and zirconia provides a balance of both. For those seeking dental crowns and bridges in Millburn NJ, the key to long-lasting results is not only the material but also regular care and professional guidance.
Resources
Alenezi, A., Aloqayli, S. Technical complications with tooth-supported fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) of different span lengths: an up to 15-year retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 23, 393 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-023-03121-9
AlMashaan A, Aldakheel A. Survival of Complete Coverage Tooth-Retained Fixed Lithium Disilicate Prostheses: A Systematic Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;59(1):95. Published 2022 Dec 31. doi:10.3390/medicina59010095